💻 Tutorial
SupraOracles is a novel, high-throughput Oracle & IntraLayer: a vertically integrated toolkit of cross-chain solutions (data oracles, asset bridges, automation network, and more) that interlink all blockchains, public (L1s and L2s) or private (enterprises). SupraOracles provides next-generation cross-chain oracle solution such that smart contracts can access better, faster, accurate, and more secure off-chain data.
With SupraOracles, your smart contract can get secure and verifiable random numbers. Supra Verifiable Random Functions (VRFs) provides smart contracts with a secure and decentralized source of randomness that is unbiasable, unpredictable, and publicly verifiable.
In this tutorial, you will use Supra VRF to request random numbers on the Klaytn blockchain using Remix IDE.
Prerequisites
- MetaMask
- Remix IDE
- Klaytn Plugin on Remix
- Test KLAY from Faucet
Getting Started
In the following steps, you will learn how to use request random numbers in your consumer contract. Lets get started!
Step 1: Create The Supra Router Contract Interface
Firstly, add the following code to the consumer/ requester contract i.e, the contract which uses VRF as a service. You can also add the code in a separate Interface and inherit the interface in the requester contract.
interface ISupraRouter {
function generateRequest(string memory _functionSig , uint8 _rngCount, uint256 _numConfirmations, uint256 _clientSeed) external returns(uint256);
function generateRequest(string memory _functionSig , uint8 _rngCount, uint256 _numConfirmations) external returns(uint256);
}
This interface will help the consumer contract interact with the Supra Router contract and through which the requester contract can use the VRF service.
Step 2: Configure the Supra Router Contract Address
Contracts that need random numbers should utilize the Supra Router Contract. In order to do that, they need to create an interface and bind it to the on-chain address of the Supra Router contract.
For Klatyn Baobab TestNet, the address is: 0x473ab8E0FC37CFf3c64ee72C2Aecf3925c2EC086
We’ll store the address within the constructor and use it later to interact with the interface.
contract SampleSupraVRF {
address supraAddr;
constructor() {
supraAddr = 0x473ab8E0FC37CFf3c64ee72C2Aecf3925c2EC086;
}
mapping (uint256 => string ) result;
mapping (string => uint256[] ) rngForUser;
}
Step 3: Use the VRF service and request a Random Number
In this step, we'll use the “generateRequest” function of the Supra Router Contract to create a request for random numbers. There are two modes for the "generateRequest" function. The only difference between them is that you can optionally provide a client-side input, which will also be part of the payload being threshold signed to provide randomness.
The generateRequest function has the following parameters viz:
- _functionSig - a string parameter, here the requester contract will have to pass the function signature which will receive the callback i.e., a random number from the Supra Router Contract. The function signature should be in the form of the function name following the parameters it accepts. We'll see an example later in the document.
- _rngCount - an integer parameter, it is for the number of random numbers a particular requester wants to generate. Currently, we can generate a maximum of 255 random numbers per request.
- numConfirmations - an integer parameter that specifies the number of block confirmations needed before supra VRF can generate the random number.
- _clientSeed (optional) - an optional integer parameter that could be provided by the client (defaults to 0). This is for additional unpredictability. The source of the seed can be a UUID of 256 bits. This can also be from a centralized source.
Having understood this, requesting VRF using Supra Oracles requires splitting the contract logic into two functions viz:
- The request function - the signature of this function is up to the developer
- The callback function - the signature must be of the form “uint256 nonce, uint256[] calldata rngList”
function getRNGForUser(uint8 rngCount, string memory username) external {
// rngCount is the number of requested random numbers
// we want to wait for 1 confirmation before the request is considered complete/final
uint256 nonce = ISupraRouter(supraAddr).generateRequest("myCallbackUsername(uint256,uint256[])", rngCount, 1);
}
Step 4: Add the validation in the callback function of requester contract
Inside the callback function where the requester contract wants the random number (in this example the callback function is exampleCallback), the requester contract will have to add the validation such that only the Supra router contract can call the function. The validation is necessary to protect against malicious contracts/users executing the callback with fake data.
function myCallbackUsername(uint256 nonce, uint256[] calldata rngList) external {
require(msg.sender == supraAddr, "only supra router can call this function");
// Following the required logic of the function
}
Practical implementation
In the example below,
- The function getRNGForUser is using the VRF service by calling the generateRequest function of the Supra Router Contract.
- Then we store the username of the user requesting the random number mapped to the nonce returned by generateRequest.
- Then the callback function prints the random numbers requested by a specific user and it has the signature: myCallbackUsername(uint256 nonce, uint256[] calldata rngList)
Once Supra generates the random number and it is verified by the on-chain logic to be authentic,
myCallbackUsernameis executed by the Supra Router, which completes the second half of the process. The nonce from the first argument is used to look up the username that originated the request.
Create and Deploy Sample Code
Remix IDE
- Navigate to Remix IDE
- Click on
File Explorertab, create a new file nameddemoSupraVRF.solin the contracts folder - Paste the code below in your newly created file
- In Remix, click Compile contract.
- Click the Klaytn tab on your left having installed the plugin
- Select Environment > Injected Provider - MetaMask.
- In Contract, select your contract. For example, SampleSupraVRF.
- Click Deploy.
Sample Code
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
interface ISupraRouter {
function generateRequest(string memory _functionSig , uint8 _rngCount, uint256 _numConfirmations, uint256 _clientSeed) external returns(uint256);
function generateRequest(string memory _functionSig , uint8 _rngCount, uint256 _numConfirmations) external returns(uint256);
}
contract SampleSupraVRF {
address supraAddr;
constructor() {
supraAddr = 0x473ab8E0FC37CFf3c64ee72C2Aecf3925c2EC086;
}
mapping (uint256 => string ) result;
mapping (string => uint256[] ) rngForUser;
function getRNGForUser(uint8 rngCount, string memory username) external {
uint256 nonce = ISupraRouter(supraAddr).generateRequest("myCallbackUsername(uint256,uint256[])", rngCount, 1);
result[nonce] = username;
}
function myCallbackUsername(uint256 nonce, uint256[] calldata rngList) external {
require(msg.sender == supraAddr, "only supra router can call this function");
// Following the required logic of the function
uint8 i = 0;
uint256[] memory x = new uint256[](rngList.length);
rngForUser[result[nonce]] = x;
for(i=0; i<rngList.length;i++){
rngForUser[result[nonce]][i] = rngList[i] % 100;
}
}
function viewRNGForUser(string memory username) external view returns (uint256[] memory) {
return rngForUser[username];
}
}
Interact with Smart Contract
To get our random number, we have to first request for random number by calling the getRNGUser function, then view the random number by calling the viewRNGForUser function.
- getRNGUser: You need to pass the rngCount and the username argument in order to execute this function successfully. The image below illustrates this:
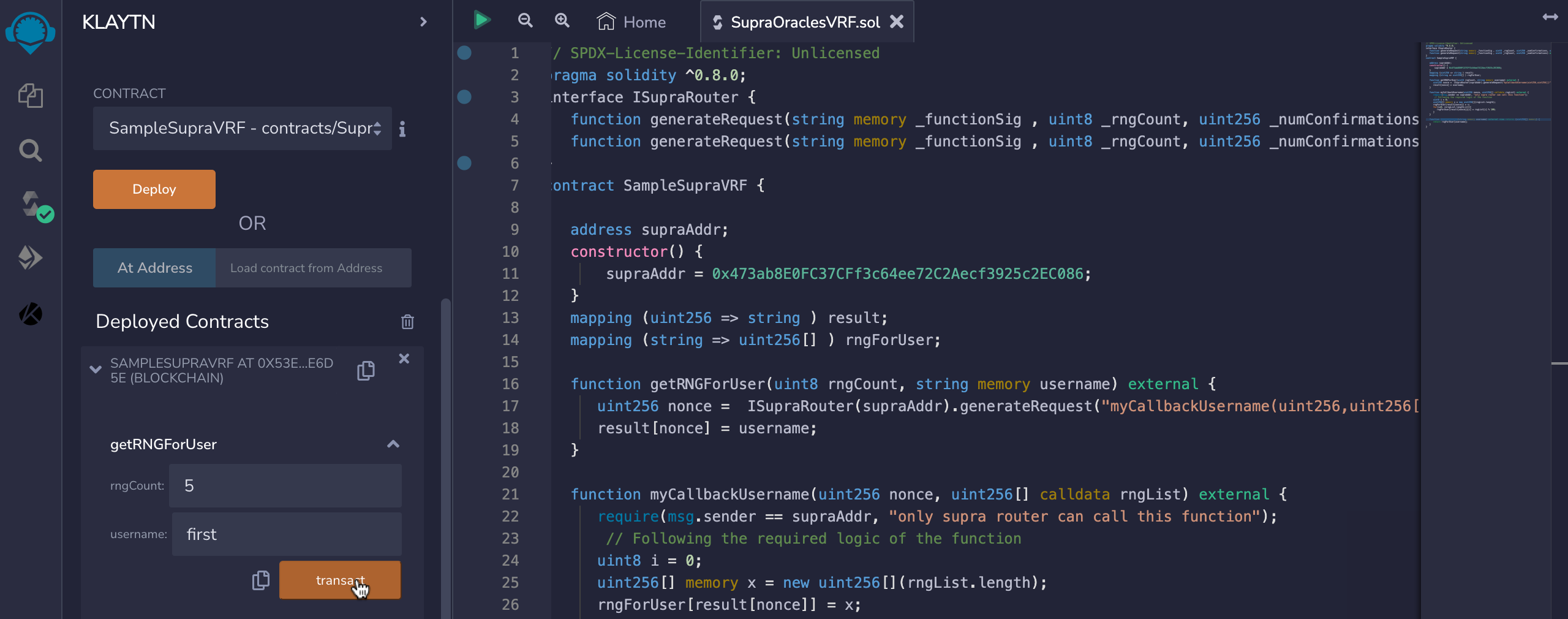
- viewRNGForUser: To view your random numbers, you need to pass in the username argument used while executing the getRNGUser function. You need to wait for few minutes for the nodes to verify this transaction.
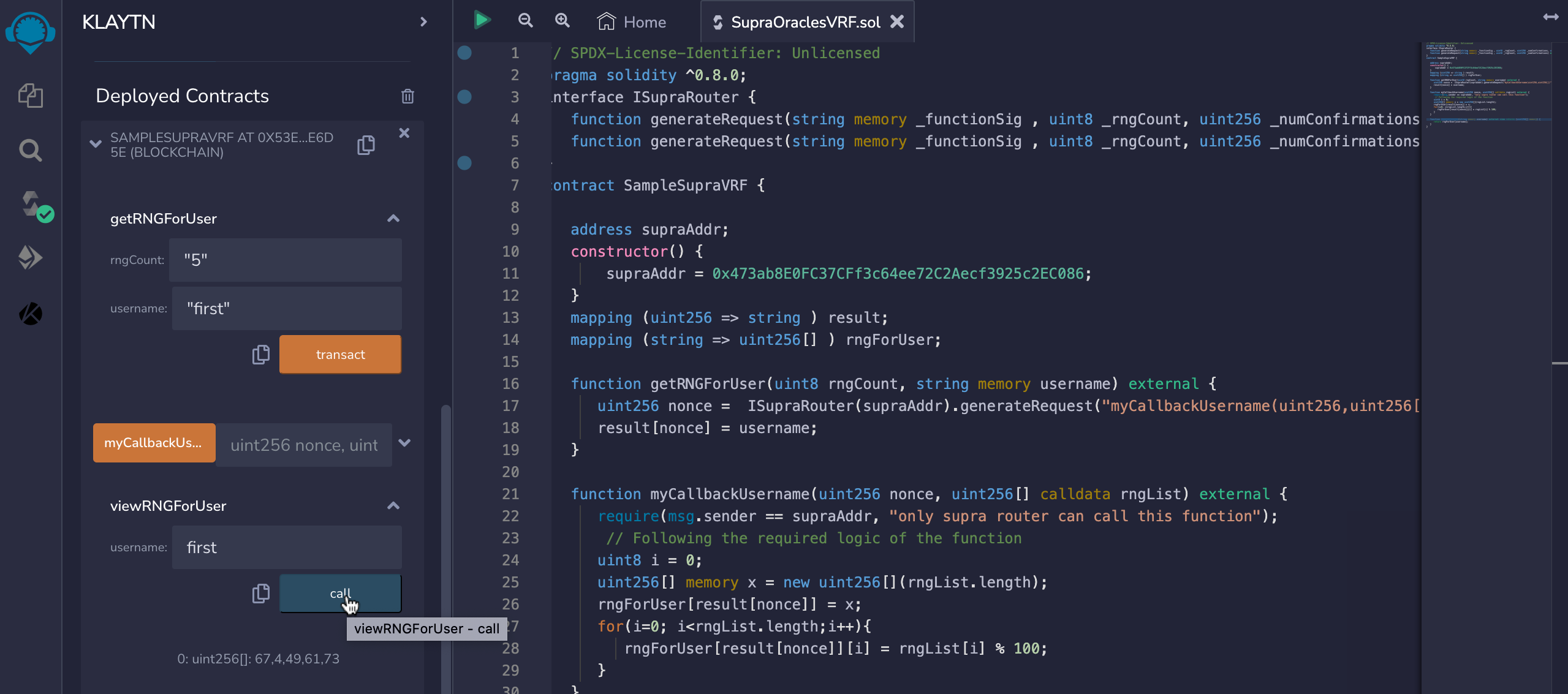
Conclusion
You have successfully requested for a random number using SupraOracles VRF on Klaytn Baobab TestNet. For additional tutorials and guides based on example use-cases, please refer to the SupraOracles Docs. If you want more information, visit Klaytn Docs and SupraOracles Docs. If you have any questions, visit Klaytn Forum.
SupraOracle integration is available only in the Baobab testnet.